Galaxies are rapidly evolving over much of the history of our universe. Key processes include gas accretion, mergers, morphology and environment. Surprisingly, the central supermassive black hole may be equally important. Our group is trying to disentangle various processes that may impact the formation of new stars in galaxies. Current studies are exploiting the rich morphological and structural information provided by the wide and deep optical imaging from Hyper-Suprime Cam on Subaru Telescope and the infrared capabilities of the James Webb Space Telescope.
To extend large spectroscopic efforts beyond z ~ 1, we carried out a large near-infrared spectroscopic survey with Subaru Telescope using the Fiber Multi-Object Spectrograph (FMOS). Over 1000 spectra yielded accurate redshifts and emission-line properties for star-forming galaxies at 1 < z < 1.7. This study is furthering our understanding of the high-redshift population in terms of global evolution, conditions of the interstellar medium (dust, ionization and metallicity), and clustering. This effort is a precursor study to the next generation multi-object spectrograph Prime-Focus Spectrograph (PFS) to be fully operational in 2025 on Subaru Telescope that will provide spectra to close to a million galaxies.
ALMA is playing an important role in our understanding of the gas/dust content and kinematics of high-redshift galaxies at 4 < z < 6 with ALPINE, and starbursts from our FMOS-COSMOS project. The large mapping of the COSMOS-Web field (CHAMPS) will provide the ISM properties with structural properties from JWST.
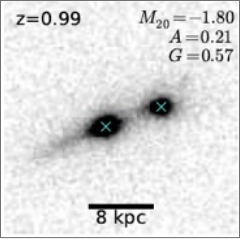
Galaxy mergers (Lackner et al. 2014)
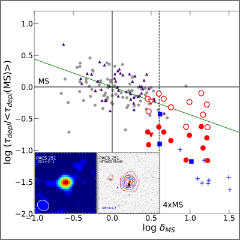
Molecular gas (Silverman et al. 2015)
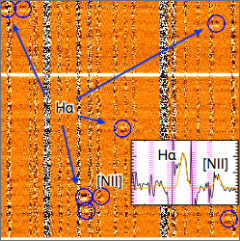
Spectroscopic surveys (Kashino et al. 2019)

Galaxy structure (Kawinwanichakij et al. 2021)
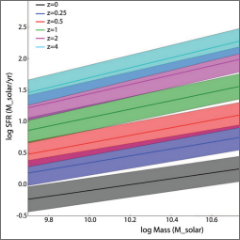
Global evolution of star formation (Speagle et al. 2014)
Kalita, B. Silverman, J. D., Daddi, E. et al. 2025, MNRAS, 537, 402
Liu, Z., Silverman, J. D., Daddi, E. et al. 2024, ApJ, 968, 15
Kalita, B., Silverman, J. D., Daddi, E. et al. 2023, ApJ, 960, 25
Kawinwanichakij, L., Silverman, J. D., Ding, X. et al. 2021, ApJ, 921, 83
Fujimoto, S., Silverman, J. D., Bethermin, M. et al. 2020, ApJ, 900, 1
Kashino, D., Silverman, J. D., Sanders, D. et al. 2019, ApJS, 241, 10
Silverman, J. D., Daddi, E., Ruojopakarn, W. et al., 2018 ApJ, 868, 75
Silverman, J. D., Ruojopakarn, W., Daddi, E. et al., 2018 ApJ, 867, 92